Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH Drone Helicopter
© Brooke Clarke 2023 |
 |
Description
Gyrodyne CN-786/ASW-20
GE 5ATY21RJ2 Aircraft AC Generator
KY-342/SRW-4C Audio Frequency Coder
Manuals
Receiving Set, AN/ARW-78
Receiving Set AN/ARW-7 (Modified)
Transmitting Set,Radio AN/URW-14A
Target Control System AN/SRW-4B
Patents
Related
References
Links
Background
Stumbled on this set of parts for the Gyrodyne QH-50 Dash Drone while looking for gyroscopes. It appears to be some QH-50 parts related to flight stability and control.
The Gyrodyne Hilicopter Historical Foundation has a number of web pages. The Dash History page itemizes all the problems, i.e. lessons learned.
My first college camera class was taught by a photographer who worked at Hiller in Palo Alto. They made the "Flying Platform" (Wiki) and Rotocycle (Wiki). The Gyrodyne RON Rotorcycle (Wiki) is a coaxial main rotor version that's very similar to the Rotocycle. The RON was a precursor to the QH-50.
There is a type of aircraft called "Gyrodyne" (Wiki) where the main rotor blade is only powered for takeoff and landing. While moving horizontally it's powered by normal aircraft propellers or jet engines. One example is the Fairey FB-1 Gyrodyne (Wiki).
In the book US Naval Weapons, Norman Friedman, 1983 (Sonobuoy Ref 19) on page 128 is a photo of a DASH with a couple of Mk 44 torpedoes. There's a history of various helicopters used in this role starting with a small Bell, then the Kaman HTK-1 (Wiki).
Description
DASH is an acronym for Drone Anti-Submarine Helicopter. The Gyrodyne (Wiki) QH-50 DASH (Wiki) was one of a number of aircraft made by the Gyrodyne of America company.
Gyrodyne CN-786/ASW-20
Fig 1 Gyrodyne CN-786/ASW-20
Fig 2 Gyrodyne CN-786/ASW-20 Gyroscope

GE 5ATY21RJ2 Aircraft AC Generator
Fig 1
Fig 2
KY-342/SRW-4C Audio Frequency Coder
Fig 1 Front Panel
Manuals
NAVAIR 01-150DHC-2-7 Maintenance Instruction Manual, Navy Model QH-50D Drone, Radio Receiving Set, AN/ARW-78, 15 May 1969
NAVAIR 01-150HC-2-7.1, Supplemental Maintenance Instruction Manual, QH-50D Drone (Modified), Radio Receiving Set AN/ARW-78, 1 March 1970
NAVAIR 16-30URW14-2, Handbook Operation Maintenance Instructions with Illustrated Parts Breakdown, Transmitting Set,Radio AN/URW-14A, 15 March 1969
NAVAIR 16-30SRW4-15 Handbook System Operation and Maintenance Instructions, Target Control System AN/SRW-4B, 15 May 1968
Patents
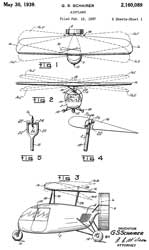
2160089 Airplane, George S Schairer, Bendix Products (Helicopters), 1939-05-30, - cab has the feel of a helicopter, pusher prop, high wing - Bendix Helicopters was sold to Gyrodyne
2177499 Aircraft, George S Schairer, Bendix Products (Helicopters), 1939-10-24, - Autogyro (Wiki)
2216164 Rotary-wing aircraft, George S Schairer, Autogiro Co, 1940-10-01, - mechanics of Autogyro hub
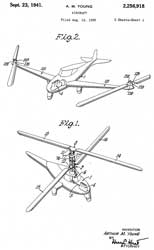
2256918 Aircraft, Arthur M Young, 1941-09-23, -
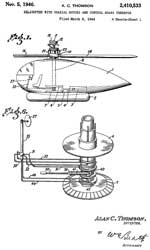
Fig 2 shows coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor2410533 Helicopter with coaxial rotors and control means therefor, Thomson Alan Charles, App: 1944-03-06, Pub: 1946-11-05, -
Turning steering wheel (27) changes pitch of blades changing heading.
2419849 Nut lock, Charles L Morris, Raytheon (United Aircraft), App: 1945-03-27, Pub: 1947-04-29, - for helicopter rotors
2456485 Helicopter with coaxial rotors, Bendix Vincent, Helicopters Inc, App: 1943-11-23, Pub: 1948-12-14, -
2475333 Helicopter, Charles L Morris, Raytheon (United Aircraft), App: 1945-03-27, Pub:1949-07-05, -
"it is an object of the present invention to provide an improved blade stop for locking the lade against flapping either upwardly or downwardly When the blade is slowed down to a predetermined degree"
2555807 Wing tip light for rotary wing aircraft, Charles L Morris, Gyrodyne, App: 1946-08-08, Pub: 1951-06-05, -
Air turbine has the look and feel of water turbine used in the Mk 6-5 torpedo exploder.
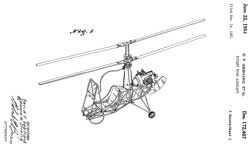
D172467 Rotary wing aircraft, D. F. Gebhard, Edward W. Strong, Gyrodyne,1954-06-22, -
coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor, Porsche engine?, one man, open frame
Gyrodyne RON Rotorcycle (Wiki)?
D166851 Cargo-carrying rotary wing aircraft and the like, Geoffrey G. Clewlow, Gyrodyne, 1952-05-27, -
D168652 Rotary wing aircraft, Peter J. Papadakos, 1953-01-20, - coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor
Might be a Gyrodyne (Wiki).
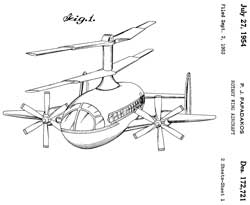
D172721 Rotary wing aircraft, Peter J. Papadakos, 1954-07-27, - coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor, a propeller on each wing
Might be a Gyrodyne (Wiki).
2629567 Helicopter rotor control system, Nicholas J Papadakos, Gyrodyne, 1953-02-24, - looks complicated
Steering Wheels 65 (steering), 66 (swash plate tilt) & 814 (collective pitch) produce changes of pitch of the rotor blades, either collectively or cyclically as well as changes in tail rotor positioning and tail rotor blade pitch.
Hand crank 434 tilts the tail rotor.
Hand crank 444 is for Longitudinal balancing.
Hand lever 820 is for collective pitch.
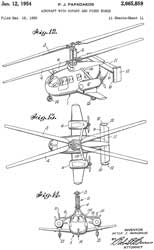
2665859 Aircraft with rotary and fixed wings, Papadakos Peter James, 1954-01-12, - coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor
Might be a Gyrodyne (Wiki).
2704128 Tail rotor mounting and control means for rotary wing aircraft, Nicholas J Papadakos, Gyrodyne, 1955-03-15, - conventional main and tail rotors
Control system from 2629567 above.
2770149 Transmission, particularly for helicopter rotors, Losey Arthur Marquis, Gyrodyne,1956-11-13, -
2815820 Power folding rotor blade system for rotary wing aircraft, Peter J. Papadakos, Gyrodyne,1957-12-10, -
to make a smaller footprint when storing.
2829721 Directional control system for rotary wing aircraft having contra-rotating load-carrying rotors, David F Gebhard, Gyrodyne, 1958-04-08, - coaxial main rotors, no tail rotor
Collective pitch lever (17) and overhead stick (18) for cyclical pitch.
Rudder pedals (33) control spoilers at the tip of the top or bottom rotor.
Has the feel of the common helicopter control system.
Gyrodyne RON Rotorcycle (Wiki)?
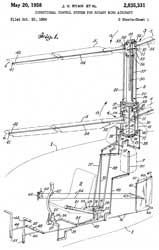
2835331 Directional control system for rotary wing aircraft, James V Ryan, Edward W Strong, Losey Arthur Marquis, Gyrodyne,1958-05-20, -
Has the feel of the common helicopter control system.
uses tip brakes (41) for heading change.
2980186 Rotor control system for helicopter, Edward W Strong, Pappas Alexander James, Losey Arthur Marquis, Clewlow Geoffrey Griffiths, Gyrodyne, 1961-04-18, - for a rotor with 3 or more blades. All the prior art Gyrodyne brand helicopters have had 2 blade rotors.
3347095 Atmospheric static pressure detection means, Edward W Strong, Richard S Reade, James E Manuel, Bastedo Walter, Gyrodyne, 1967-10-17, - mounts the Pitot tube above the rotor blade - works properly in "no wind hover at ground effect".
The Navy contract for the QH-50C included the use of aGFE radar altimeter that did not work so a static barometric pressure type was used, but that required a special static pressure port, hence this invention.
3814351 Coaxial rotor yaw control, R Bielawa, Raytheon (United Aircraft), 1974-06-04, -
"More particularly it is an object of this invention to provide yaw control in coaxial counter rotating rotors by providing telescoping blade tip portions which are deferentially operated to extend the tip portions of one rotor while retracting the tip portions of the other rotor."
5310314 Directional control system for rotary wing aircraft, Walter Bastedo, Alex Pappas, Martin L. Stevens, 1994-05-10, - rather that using blade pitch to rotate the body of the helicopter, tip brakes on one or the other rotor blade would have the same effect. So this method of changing heading applies to choppers with 2 or more main rotors.
Related
Aircraft
Ballistics
Barometers & Altimeters
Cars
Gyroscopes
Sonobuoys
Submarines
Torpedoes, mines, depth charges, &Etc
Ukiah - Helicopter photos from my house - and scroll down, Kaman K-Max,
Wind Speed
References
Ref 1. Survey of the QH-50 DASH system by Paskulovich, Robert S., Naval Postgraduate School, master's thesis, 94 pgs -
Ref 2. Not What You Think: Evolution of US Navy Destroyers - A Complete Guide, 28:04 - @14:23 Mitscher Class & testing Gyrodyne QH-50
Ref 3.The Bizarre Nazi Machine Discovered on a Secret Submarine - Rotor kite (Wiki) Focke-Achgelis Fa 330 (Wiki)
Ref 4. What Are Those Domes On The Superstructures of the Battleships?, 8:44 - drone used on Battleship to spot big guns. QH 50 aka "Snoopy"
Ref 5. The Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH: An Early Drone Helicopter That Pushed Technology Forward, 5:08 -
Ref 6. QH50 Dash Man -
Ref 7. The Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH; The Flop That Could Have Been Great?, 20:21 -
Links
PRC68, Alphanumeric Index of Web pages, Contact, Products for Sale
Page Created 2021 April 21